What is a supermoon? When to watch and what to expect
What is a supermoon? When to watch and what to expect
The vastness of the universe has always captured our attention, inspiring us to investigate and comprehend the heavenly bodies that are all around us. The Moon is one such celestial companion that has enthralled people for millennia. Many people are curious in the distance between Earth and the Moon and the significance it has in our cosmic journey as it hovers luminously in the night sky. We shall begin on an educational excursion in this post, deciphering the Earth-Moon separation and revealing the secrets hidden beneath the clear skies.
A Blue Moon and a supermoon will combine to form a full Moon on August 30. This unusual occurrence won't happen again until 2037.
What is a supermoon?
The Moon's perigee, or closest approach to Earth in a month, occurs around this time. This occasionally happens during a full Moon. It then turns into a supermoon. A supermoon is more noticeable than a regular full moon because it is significantly bigger and brighter. The full Moon on August 30 is a supermoon because it occurs at the same time as the Moon's perigee.
What is a blue supermoon?
The expression "once in a blue Moon" is frequently used to describe extremely unusual occurrences. But the definition of a "Blue Moon" in everyday usage has nothing to do with the Moon actually turning blue. There are two other definitions in its place. According to NASA, the more typical definition of a blue moon is when a full Moon appears twice in a month. The full Moon on August 30 is a blue moon because there was a full Moon on August 1 as well.
How rare is a blue supermoon?
A blue Moon by itself is a rather uncommon occurrence. The American space agency estimates that it occurs on average once every two and a half years. Given that 29 days between full moons and that months often have 30 or 31 days, there is a good chance that two full moons will occur in a given month.
Supermoons occur much more frequently. Every year, three to four are to be anticipated. A blue moon that also happens to be a supermoon is an extremely unusual occurrence. While the subsequent blue Moon won't appear until August 2023. Interestingly, NASA predicts that the next two super blue moons will occur in January and March of 2037, practically immediately following one another.
1. The Celestial Dance:
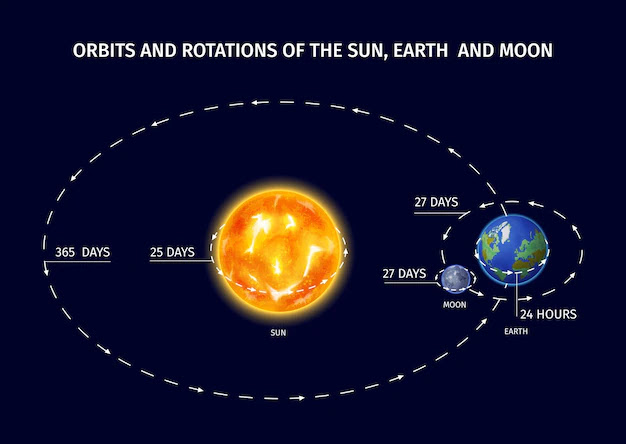
Due to gravity, the Earth and the Moon perform a mesmerizing cosmic dance. How far away are they, though? 384,400 kilometers (238,900 miles) is the average distance between Earth and the Moon. Due to the Moon's elliptical orbit around the Earth, this value represents an average. The distance between the Moon and Earth during perigee, or its closest point, is 363,300 kilometers (225,622 miles). On the other hand, it can be as far away as 405,500 kilometers (251,900 miles) at its furthest point, which is called the apogee.
2. Measuring the Earth-Moon Distance:
The astronomers Giovanni Battista Riccioli and Francesco Maria Grimaldi made the first accurate measurement of the Earth-Moon distance in the 17th century. They measured the minor shift in the Moon's apparent position against the background of stars while seeing it from various locations on Earth's surface using the parallax technique. The Earth-Moon distance is now calculated using a variety of contemporary techniques, such as laser ranging, radar observations, and lunar expeditions.
3. Laser Ranging:
The distance between the Earth and the Moon can be measured with extreme accuracy using laser ranging. It entails directing a laser beam at retroreflectors positioned during the Apollo missions on the Moon's surface. Scientists can determine the distance with astounding accuracy by accurately calculating the amount of time it takes for the laser light to reflect back to Earth. This method continues to advance our knowledge of the Moon's orbit while providing priceless information on the Earth-Moon distance.
4. Radar Measurements:
The Earth-Moon distance is largely determined by radar readings. Scientists can measure the round-trip time and use the speed of light to calculate the distance by bouncing radio waves off the Moon's surface and tracking the return of the signal. Radar measurements can be made day or night, regardless of the weather, and they are dependable and independent ways to validate laser ranging results.
5. Lunar Missions:
Our understanding of lunar geology has been enhanced by human study of the Moon, which has also provided opportunity to improve our comprehension of the Earth-Moon distance. Seismometers were positioned on the lunar surface during the Apollo missions to record seismic waves caused by impacts or moonquakes. Scientists could learn more about the internal structure of the Moon and its gravitational relationship with Earth by examining these seismic signals.
6. The Influence of Gravity:
The force that connects Earth and the Moon and controls their motion is called gravity. The Moon is kept in orbit by the gravitational attraction of the Earth, which stops it from slipping out into space. The Earth's tides are also caused by gravitational attraction. The oceans swell as a result of the Moon's gravitational influence, producing high tides. Different portions of the Earth experience the Moon's gravitational pull as it revolves on its axis, causing the tides' cyclical ebb and flow.
7. The Significance of Earth-Moon Distance:
There are several scientific and practical ramifications to the Earth-Moon distance. As a stepping stone for upcoming manned expeditions to other celestial bodies, the Moon has been essential for space exploration efforts. Planning satellite orbits, computing launch trajectories, and even foretelling lunar and solar eclipses all require knowledge of the Earth-Moon distance. Additionally, analyzing the dynamics of the Earth-Moon system allows researchers to improve their understanding of gravitational interactions and celestial mechanics.
Read also :- the acid reflux diet guide to bmanaging.html
Conclusion:
We travel beyond the azure skies as we unravel the mystery of the Earth-Moon separation, learning about the complex dance of celestial entities and the forces that control them. The roughly 384,400 km separation between Earth and the Moon has been determined using a variety of techniques, such as laser range, radar surveys, and lunar expeditions. Satellite orbits, celestial mechanics, and space exploration can all benefit from our knowledge of this separation. The Earth-Moon distance is nevertheless an intriguing feature of our cosmic neighborhood as we work to understand the cosmos' secrets, serving as a constant reminder of the universe's size and interconnection.
FAQS :-
Q1. Is it rare to see a supermoon?
Answer : Supermoons don't happen frequently, but they're also not very common either. They happen a few times a year on average. A supermoon occurs when a full moon occurs at the same time as the moon's eccentric orbit brings it closest to Earth, making it look larger and brighter in the night sky. To find out when the next supermoon will happen in your location, it's a good idea to consult a lunar calendar as the frequency of supermoons might change from year to year.
Q2. What happens when you see a supermoon?
Answer : A supermoon is a full moon that is bigger and brighter than a regular full moon when you view one. This happens as a result of the moon's somewhat elliptical orbit around Earth, which causes it to pass closer to and farther from our planet at different times (perigee and apogee).
A supermoon occurs when the moon is at or very close to its closest point to Earth (perigee), making it appear up to 30% brighter and 14% larger than a typical full moon. This phenomena typically results in enhanced moonlit landscapes and fantastic opportunities for moonwatching and photography, as well as a gorgeous and fascinating sight in the night sky. Supermoons are rare yearly occurrences that can be fascinating celestial events for astronomy aficionados and skywatchers.
Q3. Do supermoons affect people?
Answer : There are no major or scientifically verified direct physical or physiological consequences on people caused by supermoons. While supermoons can be visually stunning and awe-inspiring, there isn't much evidence to support the idea that they have a significant impact on people's emotions, behaviors, or health.
It's important to remember, too, that the moon has historically been linked to cultural and mythological notions about how it might affect people's conduct, such as the notion of the "lunar effect" or "moon madness." These statements, however, are not well supported by science.
In conclusion, supermoons are largely an astronomical and visual event, and they do not significantly affect people outside of their aesthetic appeal and potential as a source of inspiration for astronomy and photography.
Q4. Can we see supermoon in India?
Answer :Supermoons are visible in India, just like they are in many other places throughout the world. When they happen, supermoons can be seen from many places throughout the world, including India. A supermoon's visibility is influenced by a variety of variables, including the moon's phase, the season, and the local weather.
You can check astronomical calendars, moon phase applications, or speak with nearby astronomy clubs or observatories to find out when a supermoon will be visible from a particular area in India. Remember that supermoons are not incredibly uncommon occurrences and happen a few times a year, so if you're interested in moon-watching, you'll have numerous opportunity to witness them.






Post a Comment